The Groq LPU™ Inference Engine is a specialized processing system developed by Groq to handle computationally intensive applications, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs). The LPU stands for Language Processing Unit™ and is designed to provide exceptional sequential performance, high accuracy, and instant memory access.
It aims to overcome bottlenecks in LLMs related to compute density and memory bandwidth, offering faster text generation compared to traditional processors like GPUs
Groq allows you to use for free the LLMs : Llama-2 and Mistral, the latest one started to be known after Microsoft invested in them.
Groq allows you to chat with both LLMs for FREE and see how fast things are. Lately, Groq released the API that will allow you to build apps on top of it and harvest the speed that Groq has.
Groq has also a playground similar to OpenAI that will allow you to chat with the LLMs and add system roles.
Video with Groq API, Mistral and Streamlit
How To Use Groq API with Python
Groq has a Python package that can be used, you just need to install it with:
pip install groq
After you can use it as below:
Imports
- import os: This imports the standard
oslibrary, which provides ways to interact with the operating system. It’s used here to access environment variables. - from groq import Groq: Imports the necessary
Groqclass from the Groq Python library for interacting with the Groq API.
API Key Setup
client = Groq(
api_key=os.environ.get("GROQ_API_KEY"),
)
api_key=os.environ.get("GROQ_API_KEY"): This retrieves the Groq API key stored in an environment variable named “GROQ_API_KEY”. It’s a more secure way of managing the API key than including it directly in the code.client = Groq(...): This creates a Groq client object, which is your primary way of interacting with the Groq API.
Chat Completion Function
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="mixtral-8x7b-32768",
messages=[ ... ],
temperature=0.5,
max_tokens=5640,
top_p=1,
stream=True,
stop=None,
)
- client.chat.completions.create(): This function call initiates a chat completion task using the Groq API. It’s designed for generating conversational text responses.
- model=“mixtral-8x7b-32768”: Selects a specific Groq language model for the task.
- messages=[…]: A list defining the initial conversation structure:
"role": "system": Designates a system message."content": "...": Provides instructions that tell the model to act like a YouTube expert focused on generating titles for a given keyword
- temperature=0.5: Controls randomness in output. Lower values lead to more predictable results.
- max_tokens=5640: Sets a maximum limit on the number of tokens (roughly words or word parts) in the generated response.
- top_p=1: Influences the sampling of tokens during generation.
- stream=True: Requests that the output is streamed as it’s generated, rather than providing the entire output all at once.
- stop=None: No specific stop sequence is indicated.
Output Handling
for chunk in completion:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content or "", end="")
for chunk in completion: Iterates over the streamed results from the chat completion task.print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content or "", end=""):- Prints the content of the first suggested title (
chunk.choices[0]). - The
or ""handles cases where there might not be content. end=""prevents adding a newline after each title, keeping the output in a single line.
- Prints the content of the first suggested title (
An example of complete code would be:
import os
from groq import Groq
client = Groq(
api_key=os.environ.get("GROQ_API_KEY"),
)
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="mixtral-8x7b-32768",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a YouTube expert creator who likes to write engaging titles for a keyword. \nYou will provide 10 attention Grabbing Youtube titles on keywords specified by the user."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Install WordPress on Docker"
}
],
temperature=0.5,
max_tokens=5640,
top_p=1,
stream=True,
stop=None,
)
for chunk in completion:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content or "", end="")
The above will provide 10 YouTube video titles for the video Install WordPress on Docker. And if you run it you will see that results are provided very fast.
How To Use Groq API with Streamlit
If you want to add a UI to your Python code you can do that easily with Streamlit or any other Python UI Library
First, thing will be to install Streamlit near Groq:
To do that for my previous example you will have a code like:
pip install streamlit
Then you will have the Python with Streamlit code:
import os
import streamlit as st
from groq import Groq
# Function to get Groq completions
def get_groq_completions(user_content):
client = Groq(
api_key=os.environ.get("GROQ_API_KEY"),
)
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="mixtral-8x7b-32768",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a YouTube expert creator who likes to write engaging titles for a keyword. \nYou will provide 10 attention-grabbing YouTube titles on keywords specified by the user."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": user_content
}
],
temperature=0.5,
max_tokens=5640,
top_p=1,
stream=True,
stop=None,
)
result = ""
for chunk in completion:
result += chunk.choices[0].delta.content or ""
return result
# Streamlit interface
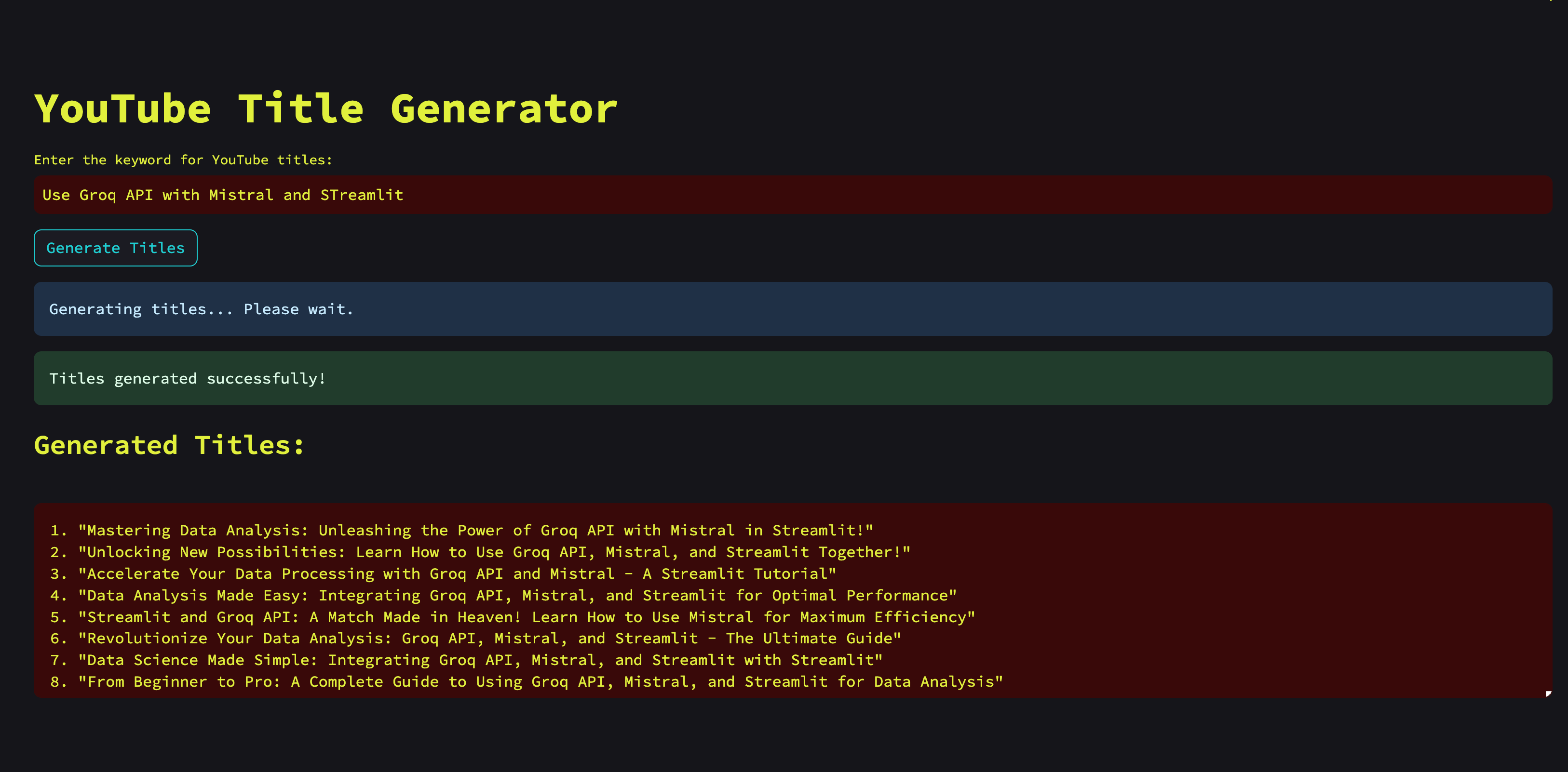
def main():
st.title("YouTube Title Generator")
user_content = st.text_input("Enter the keyword for YouTube titles:")
if st.button("Generate Titles"):
if not user_content:
st.warning("Please enter a keyword before generating titles.")
return
st.info("Generating titles... Please wait.")
generated_titles = get_groq_completions(user_content)
st.success("Titles generated successfully!")
# Display the generated titles
st.markdown("### Generated Titles:")
st.text_area("", value=generated_titles, height=200)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The Streamlit-Mistral-Groq code was generated with the help of ChatGPT as I don’t know that well either of the codes but is fully functional. You can use AI tools to help you build some things. At the end you can go and run the Streamlit App with
streamlit run app.py
When you are ready you can go and deploy the app for free in Streamlit Cloud or on your own VPS with: Deploy Streamlit on a VPS and Proxy to Cloudflare Tunnels
Conclusions
Groq can help you build very fast AI applications because of their faster LPU and Mistral is an LLM that is not for behind ChatGPT 4, you can use both FREE and see if they are useful to you.
I hope this article motivated you to start and see what both have to offer.



