Deploying a Python uv Project with Git and Railpack in Dokploy
See how you can host your project easily with Dokploy, Railpack, and uv

Dokploy is an open-source platform that simplifies deploying applications on your VPS using Docker and Traefik. With its Git integration and support for Railpack—a versatile build provider—you can deploy Python projects managed with uv effortlessly. In this guide, we’ll deploy a FastHTML-based Python project using Git and Railpack within Dokploy, detailing the project setup, Railpack configuration with railpack.json, and deployment steps.
In the past I have covered dokploy installation and uv get started + fasthtml get started, you can check them for more details on each.
Dokploy, Railpack, and uv form a powerful stack for self-hosted Python deployments. Let’s get started!
What Are uv, Railpack, and Dokploy?
uv
uv, developed by Astral, is a Rust-based Python package and project manager that outperforms tools like pip and poetry. It’s 10-100x faster at resolving and installing dependencies, using a uv.lock file for reproducibility and pyproject.toml for configuration.
Railpack
Railpack builds and deploys applications, supporting Python with package managers like uv. It detects Python projects via files such as main.py or pyproject.toml, installs dependencies, and configures a production environment using a railpack.json file if provided.
Dokploy
Dokploy is a self-hosted deployment solution that orchestrates applications via Docker, with Traefik for routing and load balancing. It supports Git-based deployments and multiple build types, including Railpack, allowing you to push code to a repository and have Dokploy build and deploy it automatically.
Deploying a Python uv Project with Git and Railpack in Dokploy
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- Dokploy installed on a VPS (follow the installation guide).
- uv installed locally (
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh). - Git installed locally and a Git repository (e.g., GitHub, GitLab).
- Docker running on your Dokploy server (included by default).
- Access to your Dokploy dashboard (e.g.,
http://your-server-ip:3000).
We’ll deploy a FastHTML app as an example.
Step 1: Set Up Your uv-Managed Python Project
Create a Python project with uv and FastHTML.
-
Initialize the Project
uv init my-fasthtml-app cd my-fasthtml-appThis generates:
my-fasthtml-app/ ├── .python-version # e.g., "3.12" ├── main.py # Starter script ├── pyproject.toml # Project config └── README.md # Documentation -
Add Dependencies Install FastHTML:
uv venv source .venv/bin/activate uv add python-fasthtmlThis updates
pyproject.tomland creates auv.lockfile. -
Write a FastHTML App Edit
main.py:from fasthtml.common import * app, rt = fast_app() @rt("/") def get(): return Div(P("Hello from uv and Dokploy!")) serve() -
Test Locally
uv run main.pyVisit
http://localhost:5001to verify it works. -
Initialize Git
git init git add . git commit -m "first commit" git branch -M main git remote add origin [email protected]:user/my-fasthtml-app.git git push -u origin main
Step 2: Configure Railpack for Dokploy
Railpack detects Python projects via main.py, pyproject.toml, or uv.lock and supports uv natively. You don’t need to do anything but railpack.json file can be used to customize the build and deployment for more advanced configurations.
Understand Railpack Defaults
- Detection: Recognizes
main.py,pyproject.toml, anduv.lock. - Versions: Defaults to Python 3.13.2, overridable with
.python-versionorRAILPACK_PYTHON_VERSION. - Install: For
uv.lock, Railpack usesuvto install dependencies (assumed to beuv sync). - Start: Defaults to
python main.pyif no framework is detected. - Runtime: Sets variables like
PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1.
Step 3: Set Up Dokploy with Git
Deploy using Dokploy’s Git integration and Railpack.
-
Log In to Dokploy Open your dashboard (e.g.,
http://your-server-ip:3000). -
Create a New Project
- Go to Projects > New Project.
- Name it
my-uv-appand save.
-
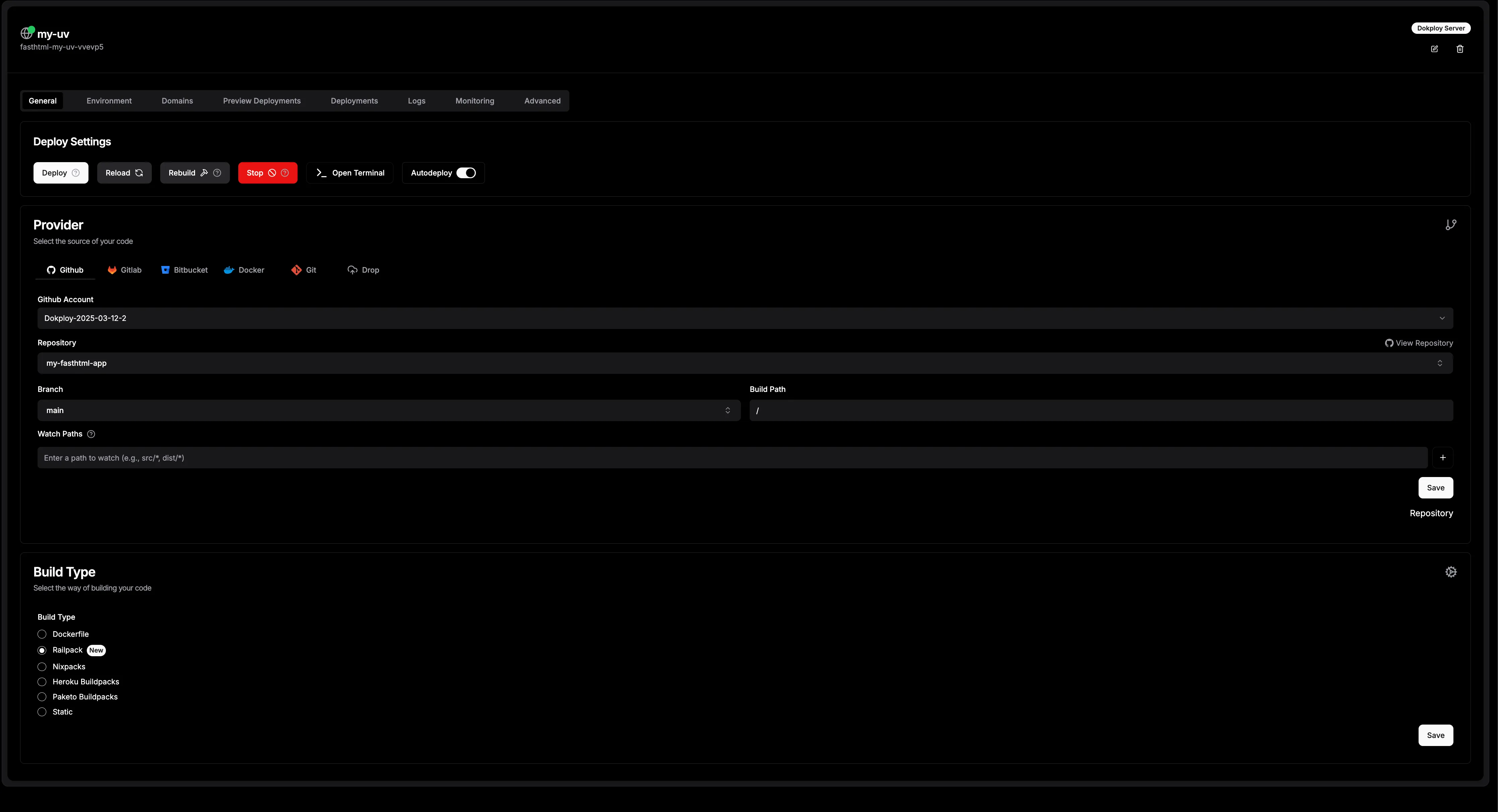
Add an Application
- Click New Application.
- Name:
my-uv-app. - Git Repository:
https://github.com/yourusername/my-uv-app.git. - Branch:
main. - Build Type: Railpack (select custom if Railpack isn’t listed).
- Save.
-
Configure Environment Variables (Optional)
- In the Environment tab, add what env varialbes you need for your project.
-
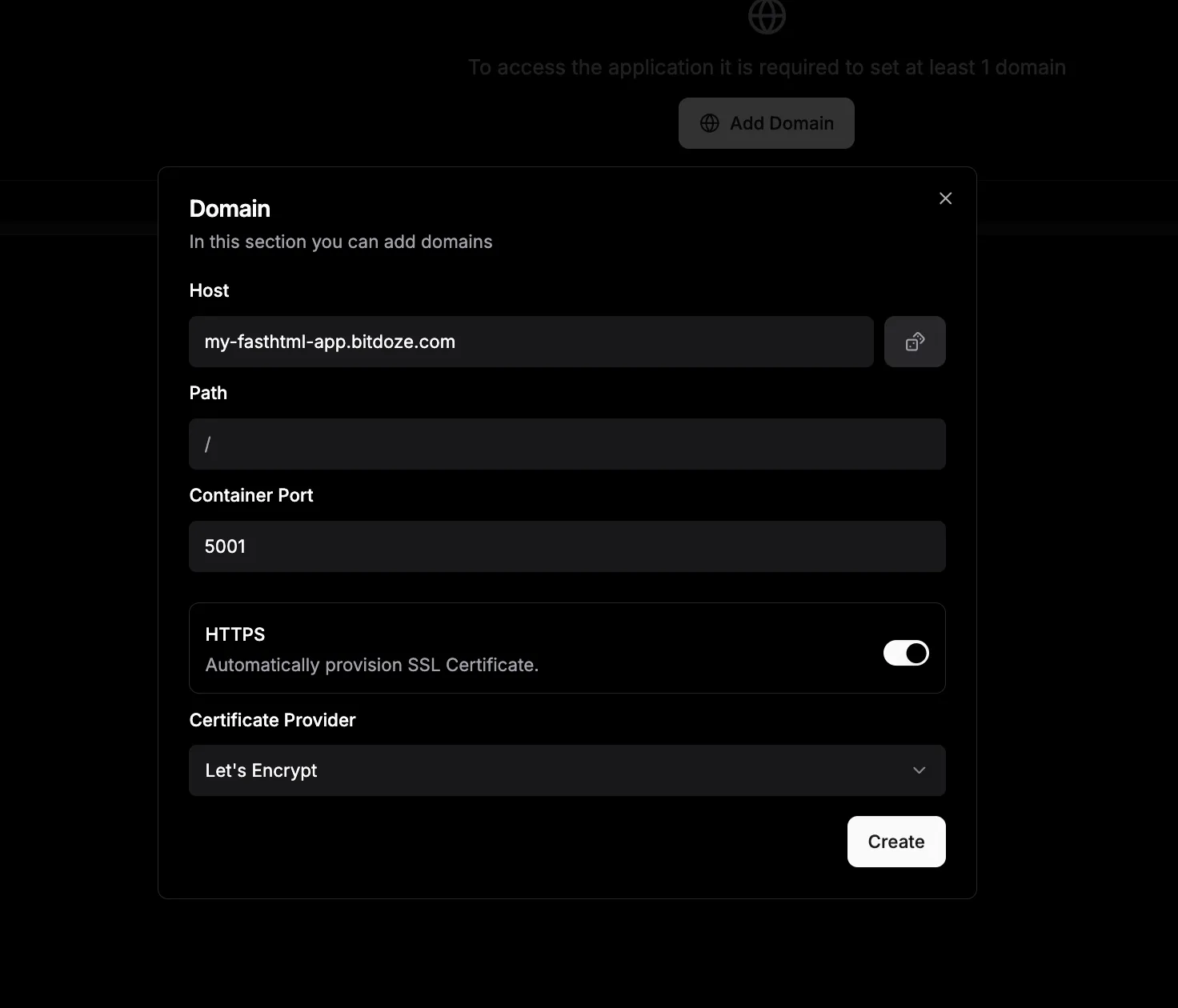
Set Up a Domain
- In the Domains tab, add a custom domain (e.g.,
my-uv-app.yourdomain.com) be sure the domain is properly configured. - Enable HTTPS for custom domains.
- In the Domains tab, add a custom domain (e.g.,
- Deploy the Application
- Click Deploy.
- Dokploy clones the repo, uses Railpack to build, and deploys the container.
Step 4: Verify the Deployment
-
Check the Logs
- In the Logs tab, confirm
uv syncand the app starting.
- In the Logs tab, confirm
-
Test the App
- Visit your URL (e.g.,
http://my-uv-app-yourserver.dokploy.app). - Expect:
<div><p>Hello from uv and Dokploy!</p></div>.
- Visit your URL (e.g.,
Step 5: Automate Future Deployments
-
Enable Auto-Deploy
- In settings, enable Auto Deploy for
main. - Push updates to trigger redeployments.
- In settings, enable Auto Deploy for
-
Example Update Edit
main.py:@rt("/") def get(): return Div(P("Updated: Hello from uv and Dokploy!"))git add main.py git commit -m "Update greeting" git push origin main
Why Use Dokploy with uv and Railpack?
- Self-Hosted Flexibility: Running Dokploy on your own VPS gives you full control over your infrastructure, avoiding the constraints and costs of managed cloud platforms. You dictate the hardware, security policies, and scaling options, making it ideal for privacy-conscious projects or custom setups.
- Speed and Efficiency:
uv’s lightning-fast dependency resolution—often 10-100x quicker thanpip—pairs perfectly with Railpack’ streamlined build process, reducing deployment times significantly. This combination minimizes downtime and accelerates iteration cycles, crucial for rapid development and testing. - Automation and Workflow Integration: Git-driven deployments through Dokploy enable a seamless CI/CD pipeline. Push changes to your repository, and Dokploy automatically rebuilds and redeploys your app using Railpack, eliminating manual intervention. This automation integrates effortlessly with existing Git workflows, enhancing team productivity.
- Reproducibility:
uv’suv.lockensures consistent dependency versions across environments, while Railpack’ configuration inrailpack.jsonlocks in build and runtime steps. Together, they guarantee your app behaves the same locally and in production, reducing “works on my machine” issues. - Modern Tooling Synergy: In 2025,
uvand Railpack represent cutting-edge Python tooling, leveraging Rust’s performance and modern build practices. Dokploy ties these together with a user-friendly interface, making advanced deployment accessible without sacrificing power.
Conclusion
Deploying a uv-managed FastHTML project with Git and Railpack in Dokploy offers an efficient, customizable, and forward-thinking approach to Python application hosting. The railpack.json configuration lets you precisely define how your project is built and run, from installing uv and syncing dependencies to launching your FastHTML app. By pushing your code to a Git repository and configuring Dokploy, your application goes live on your own infrastructure in minutes—self-hosted, secure, and poised for growth.
This stack not only simplifies deployment but also empowers you with the tools to iterate quickly, scale confidently, and maintain full ownership of your environment. Whether you’re building a small prototype or a production-ready service, Dokploy, uv, and Railpack deliver a modern deployment experience tailored to 2025’s demands.

